#10 How ONDC can compete with Swiggy/Zomato ?
Breaking Barriers in Digital Commerce: A Deep Dive into India's ONDC Initiative
What is ONDC?
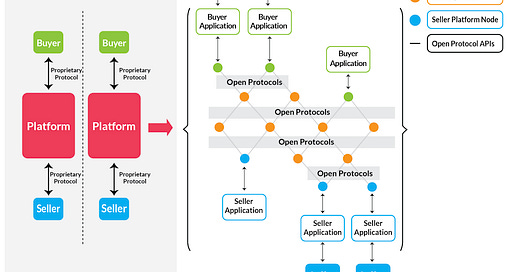
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an initiative backed by the Indian Government to reconfigure the e-commerce landscape in the country. ONDC is a unique concept - it's not an e-commerce platform but a blueprint of guidelines and rules, facilitating interoperability among various e-commerce platforms. This ensures customers have a broader scope of seller choices.
Key aspects of ONDC include:
Buyer Side Network: Companies can extend ONDC services to their customers by integrating into the network and effortlessly onboarding sellers.
Seller Side Network: Certain companies, such as Pet Pooja and Ingenio, will provide seller-side onboarding, integrating the seller catalog to the ONDC network. This integration will be used by buyer-side network companies to streamline commerce. The network also includes delivery partners such as Shadowfax, Dunzo, and Expressbees.
Technology Providers: They offer essential services like payment gateways to smoothen transactions.
What are the main problems ONDC wants to solve?
The fundamental issues ONDC intends to address are:
Boosting e-commerce penetration in India.
Creating a level playing field for SMEs by curtailing the monopoly of commerce marketplaces and their high commissions.
Making commerce more accessible and affordable for the masses by disrupting the price monopoly of commerce marketplaces and offering multiple touch points via various buyer-side apps.
Hyperlocal Food aggregator has the highest commissions and fits into the perfect problem to be solved via ONDC.
Learning from Past Attempts to Disrupt Food Delivery
Notable attempts to enter the food delivery business have been made by Amazon Food, Ola Food, and independent restaurant apps. These ventures fell short due to:
Limited Selection of Restaurants: A single restaurant's app struggles to garner consumer demand compared to a platform like Swiggy or Zomato which offers a multitude of choices. This dynamic discouraged new aggregators from entering the ecosystem.
Delivery Challenges: Without a robust delivery network like Swiggy/Zomato, restaurants faced difficulties fulfilling orders in a timely manner from their own websites.
Customer Support Issues: Given the novelty of food delivery services, there was a trust deficit in the ecosystem. Consumers leaned toward established players expecting a superior experience and reliable chat-based support.
Why do food delivery marketplaces charge commissions from sellers?
Food delivery marketplaces charge 20% commissions to restaurants to cover:
Subsidized delivery fees.
Customer support costs.
Promotional and marketing expenses.
Technology costs for maintaining a large network.
Employee salaries for different roles including sales, operations, and technology.
How ONDC will solve this problem?
ONDC's approach to resolving food delivery commerce issues includes:
Zero Customer Acquisition Cost: The integration of ONDC with established buyer-side marketplaces like Phonepe and Paytm drastically reduces the cost to acquire new food delivery customers.
Rapid Seller Acquisition: ONDC's integration with seller-side marketplaces ensures quick onboarding of restaurants and delivery partners at a minimal cost.
Incentives for Customers to Switch: With no commissions, merchants can pass on a portion of the savings to consumers, creating a price incentive to switch from other food aggregators to ONDC.
Reduced Long-term Technology Costs: Shared technology development costs, coupled with government support, reduce long-term expenses.
Navigating the Challenges: ONDC's Road Ahead
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) presents an innovative solution to streamline Indian e-commerce, yet it's not without challenges.
Delivery Experience: This represents a significant hurdle. Unlike traditional food aggregators, ONDC doesn't exercise direct control over the delivery process, instead relying on third-party delivery partners. While this model provides flexibility, maintaining consistent service quality across the spectrum of delivery partners may prove a formidable task. Nevertheless, ONDC remains optimistic about third-party delivery partners advancing and establishing robust delivery networks.
Customer Support Experience: With the adoption of open protocols and advancements in AI, ONDC anticipates a substantial reduction in support costs, aiming to provide efficient customer assistance. The challenge lies in ensuring a seamless and responsive support system. To this end, ONDC plans to bring on board technology partners to offer robust customer support across the network.
Monetization: Finally, the sustainability of ONDC hinges on its monetization strategies. On the buyer side, marketplaces plan to generate revenue through restaurant and brand advertisements, making the most of the vast consumer base. Conversely, seller-side marketplaces intend to monetize by offering services like order acceptance and catalog management to restaurants as part of a subscription model.
Despite these challenges, ONDC's innovative framework, its strategic approach to problem-solving, and its commitment to offering a seamless e-commerce experience indicate a promising future in the Indian e-commerce sector.




Hello Asad, I love your articles. Would you be interested in publishing articles to paying customers via an invite-only platform? Please drop a hi to contact@xynn.xyz and we can take this further.